By Paul Wesslund and Amy Higgins
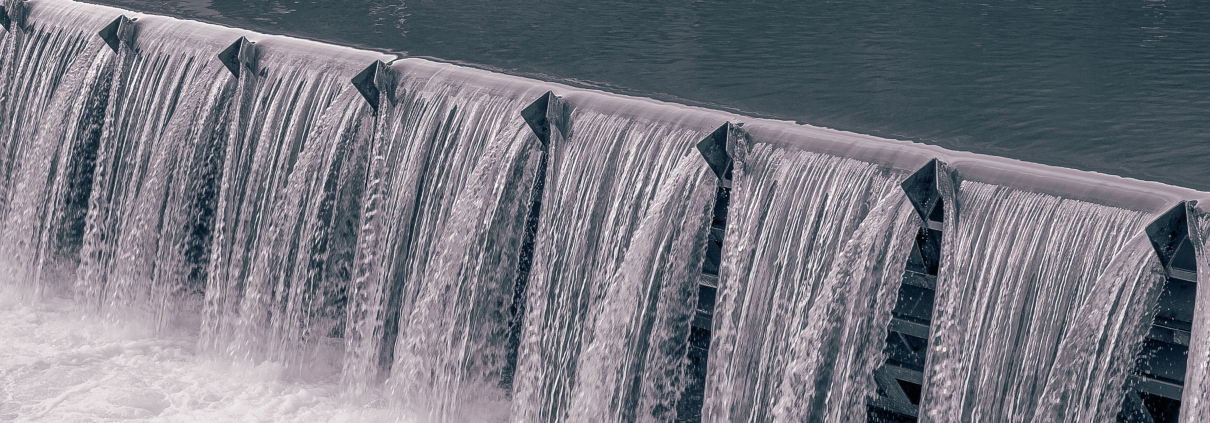
Attention to energy and the environment focuses new light on one of the oldest sources of power: falling water. “Hydropower was the first source of electrical energy used in the United States,” states a U.S. Department of Energy report issued in recent years. In fact, hydropower has always been a part of Colorado’s renewable energy mix. Today, about 30% of the power delivered by electric co-op power supplier Tri-State Generation and Transmission Association comes from renewable resources and approximately half of that 30% comes from large hydroelectric resources, which is primarily provided by the Western Area Power Administration, according to Mark Stutz, public relations specialist at Tri-State.
The DOE report concludes, “Increasing hydropower can simultaneously deliver an array of benefits to the nation that address issues of national concern, including climate change, air quality, public health, economic development, energy diversity and water security.”
 The 395-page Hydropower Vision — A New Chapter for America’s 1st Renewable Electricity Source reports that, in the next 35 years, the United States could increase hydropower production by half of what it generates today: from 101 gigawatts today to 150 GW by 2050.
The 395-page Hydropower Vision — A New Chapter for America’s 1st Renewable Electricity Source reports that, in the next 35 years, the United States could increase hydropower production by half of what it generates today: from 101 gigawatts today to 150 GW by 2050.
While this seems like a perfect energy solution, it should be noted that this projection wouldn’t make a major change in the nation’s fuel mix. Achieving that entire 150-GW goal would only raise the share of electricity produced by hydropower from about 6% today to about 9% 35 years from now. And that forecast is a best-case scenario.
Here’s what would be needed for that to happen:
• Technical innovation to improve the effectiveness of equipment that converts flowing water into electricity
• Construction of new hydroelectric dams and the conversion of existing power-producing structures into electricity generators
• Streamlining a complex web of regulations that affect construction on rivers and streams
But even though hydropower seems to have taken the back burner to solar, wind and battery storage, hydroelectricity is still an important, viable and valuable renewable energy resource.
Long term, cost effective
Tom Lovas understands the promise and the problems of hydropower. He worked on several hydroelectric projects as a technical liaison and consultant with the National Rural Electric Cooperative Association, the trade association for the country’s electric co-ops.
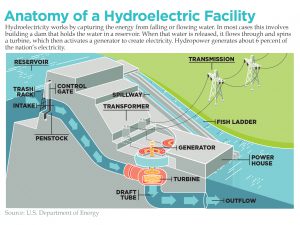 “Hydropower is a good, long-term, cost-effective resource for electric cooperatives,” Lovas says. He adds that, with environmental concerns about greenhouse gas emissions, hydropower is “certainly an avenue that should be explored.”
“Hydropower is a good, long-term, cost-effective resource for electric cooperatives,” Lovas says. He adds that, with environmental concerns about greenhouse gas emissions, hydropower is “certainly an avenue that should be explored.”
But Lovas sees cost and regulation as limiting the DOE Vision report’s lofty goals.
“There’s been relatively little new hydroelectric development in the country in a number of years in part because of the consideration of environmental aspects associated with the reservoir development,” he says. “It takes quite a bit of time and effort to get through the licensing phase of extensive feasibility studies and environmental reports, plus there’s the relatively high up-front construction cost.”
For example, Gunnison County Electric Association in Gunnison conducted a study in 2010 that showed that the nearby Taylor Reservoir Dam could support a 3.4 megawatt hydroelectric project, so GCEA decided to take on the project. Fast forward to today — nearly a decade later — and the co-op is finally nearing an agreement with the Uncompahgre Valley Water Users, according to GCEA CEO Mike McBride. “If we can get a memorandum of understanding signed — hopefully by the end of the year — we would turn our attention to permitting and design,” he says.
McBride says GCEA is also still in the permitting process with the Bureau of Reclamation, which will likely take several months. However, he explains, “Our two biggest challenges at Taylor have been in reaching a shared vision with the water users and the fact that electrical infrastructure at the dam is insufficient for a larger project.
“The 2010 (study) concluded that the water resource could support a 3.4 MW project, but there are 18 miles of singlephase distribution line from the dam to the substation that would need to be upgraded to three-phase, which would be a significant additional cost to the project,” McBride says.
GCEA is considering Taylor Reservoir Dam to be a 200- to 500-kilowatt project, which would produce between 1.6 million and 3.7 million kilowatt-hours of energy. “The fact that 6 miles of that line is under the road in a narrow section of the canyon is part of the reason that we are looking at a smaller project initially,” McBride says, adding “the project could be expanded in the future.
With hydropower, small seems to be trending. In 2017, White River Electric Association in Meeker began generating electricity with its first micro hydroelectric project using irrigation ditch water to power the project. And a Fort Collins-based Poudre Valley Rural Electric Association consumer-member has a 25-kW micro hydropower generator that powers his farm’s sprinkler during the growing season, using irrigation ditch water as well.
The DOE Vision report lists several ways to expand the use of technology that turns water into electricity. Lovas says the two most likely prospects for increasing hydropower are to modernize existing facilities and to add generation to dams and waterways that do not currently provide electricity.
“I would expect that upgrades to existing plants and adding power at existing dams and canals probably have the highest potential benefit,” Lovas says, noting that focusing on improving efficiency and effectiveness could avoid some of the problems of expense and regulatory approvals for an entirely new project.
DOE’s Vision reports that there are about 50,000 dams in the country that don’t have hydroelectric equipment. The report states that the potential of those 50,000 dams, as well as upgrades to existing plants, could provide about a fourth of its ambitious projection of 150 GW by 2050.
Storing energy from other renewable sources
Lovas also sees another area of promise for hydropower that would make solar and wind power more useful. It’s called pumped storage.
Forty-two existing pumped storage plants in the United States, including at least two in Colorado, basically allow the utilities that operate them to time-shift electricity use. When people aren’t using much electricity, like in the middle of the night, the utility uses relatively low-cost available generation capacity to pump water from a nearby reservoir to one located at a higher elevation. Then, when the utility needs extra capacity, it draws water from the upper reservoir to run a power turbine.
The DOE Vision report projects pumped storage as potentially providing 36 GW toward its 49 GW goal.
Lovas says more use of pumped storage could “help improve the economics of other renewable resources.” For example, pumped storage could provide electricity when a wind farm can’t, like in calm weather, or for a bank of photovoltaic solar energy cells at night.
“You could optimize the availability of photovoltaics by being able to store the energy,” Lovas says. “Then, the pumped storage effectively serves as an alternative to a battery.”
The problems might outweigh the promise of generating more hydropower, but utilities continue exploring viable options for more renewable energy sources.
Paul Wesslund writes on cooperative issues for the National Rural Electric Cooperative Association. Amy Higgins covers Colorado issues.